NEW FEATURES: Model validation
Innovative and strategic functionality in project and procurement coordination using BIM methodology
One of Truspace's characteristics is that it is constantly evolving with the goal of optimizing and making management processes efficient, thus meeting the needs of its various users and adopting new industry standards.
One of the recently completed research and development topics led to the release in March of the Model Validation on-board feature, a feature that introduces an automated process for ensuring data consistency in Truspace.
Telling us about the approach, the logic of operation and the benefits of this implementation is Davide Cossu of the Truspace project's R&D team.
WHAT
What do we mean by model validation?
Davide Cossu: "It is necessary to make a small premise. The design of an asset, be it a building or an infrastructure, involves an interactive and iterative collaborative process between heterogeneous and multidisciplinary teams of engineers, united by a common goal. In order for what is elaborated and produced to be homogeneous, consistent with the client's information specifications, and easily understood, it is imperative that a protocol be defined and shared in the early stages of the project.
The protocol has various names (information management plan, BEP, etc.) and within it are defined the standard conventions that will be adopted for data and information management: nomenclature, classification, hierarchies, coding, correlations, etc.
Verification that the data generated through 3D drawings are consistent with the information model is typically the responsibility of the organizational roles (BIM Coordinators, Validators) of controlling and coordinating projects carried out with BIM methodology, which therefore need support tools that highlight errors and discrepancies as soon as possible to give evidence to designers and modelers and request corrections.
Such the control activity can be very onerous given the high mass of information to be verified; on the other hand, it impacts the overall quality of the project and process.
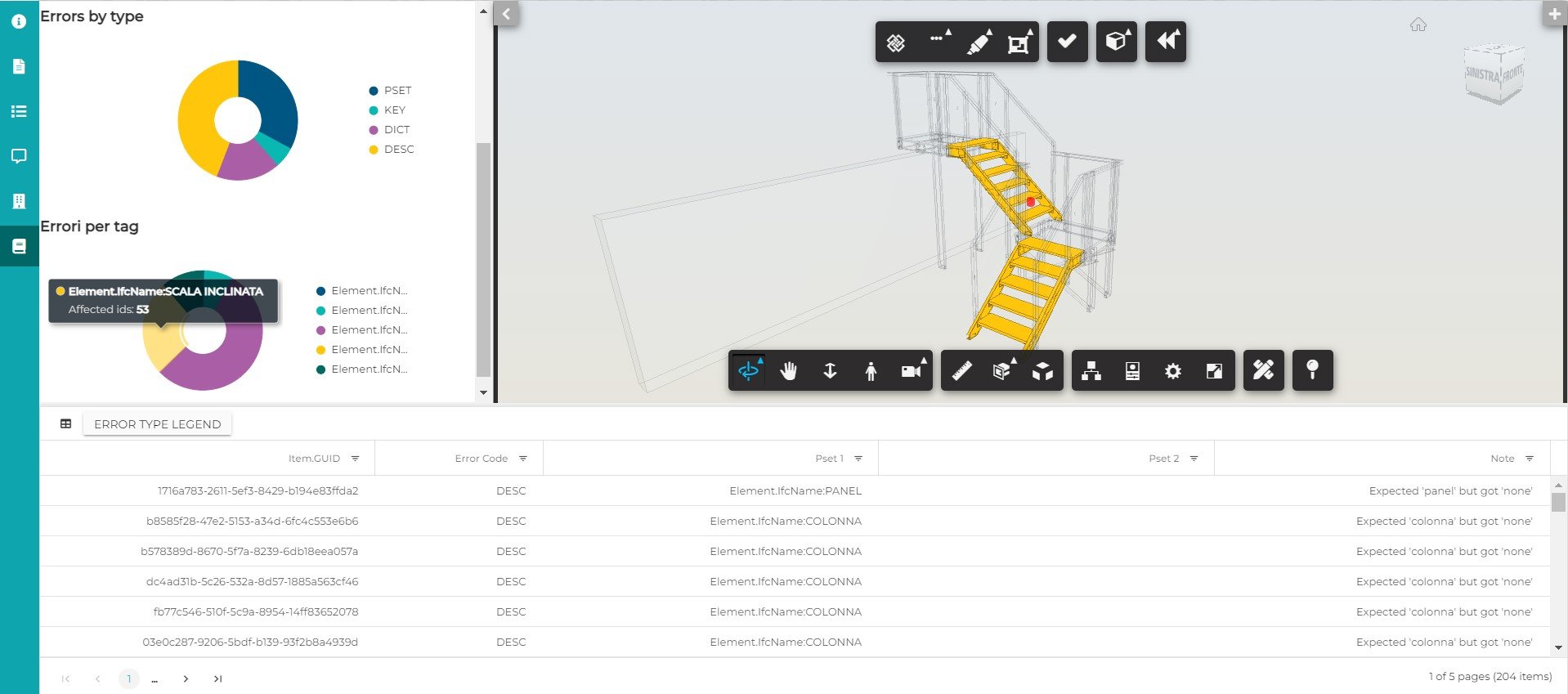
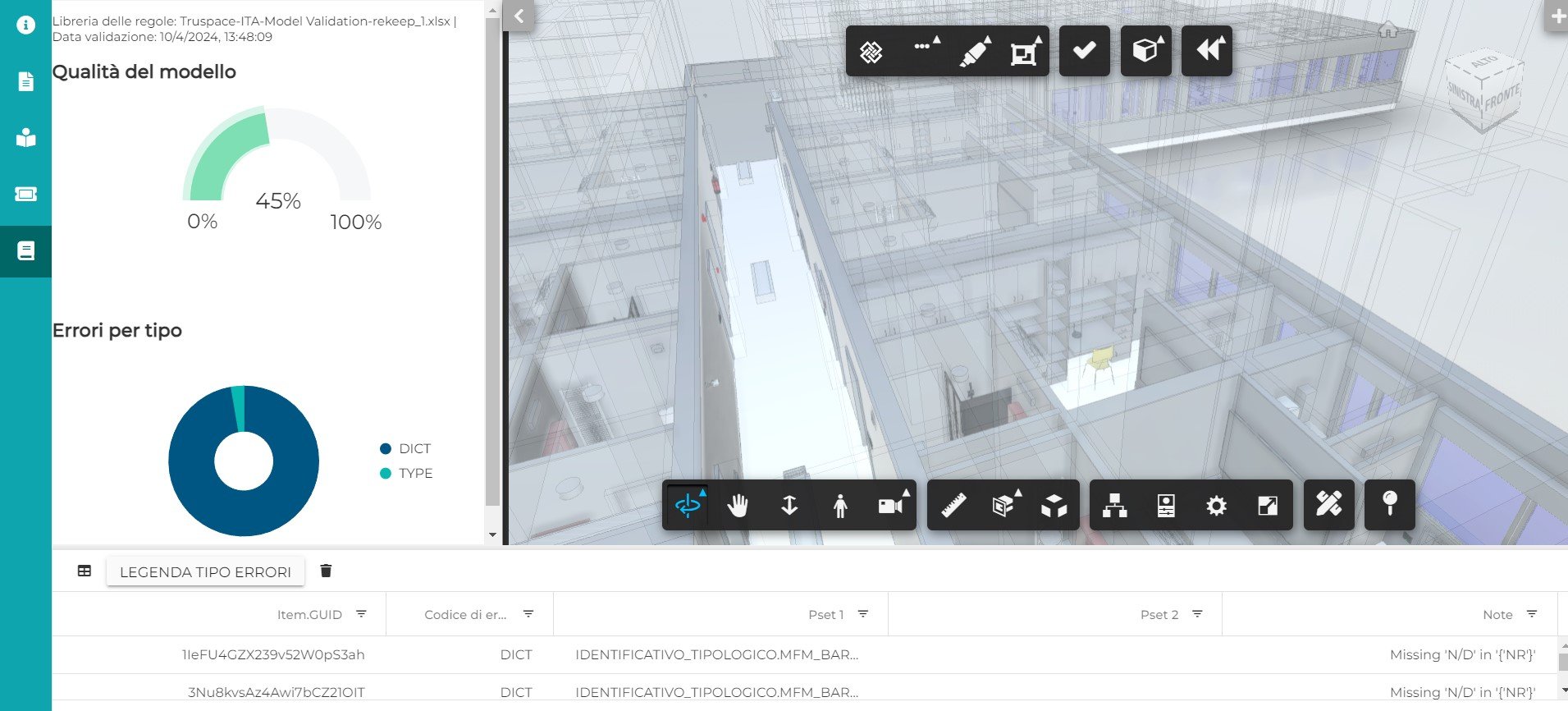
The model validation is the process aimed at detecting and highlighting errors and discrepancies in the information content of a 3D model by comparing the metadata it contains with the set of rules described in the protocol.
The method introduced in Truspace "calculates" the level of correctness of what is modeled by the specialists and uploaded to the platform, indicating an overall rate of quality and the detail of the types of errors detected, their location in the model, and the impact they have.
It is noteworthy that this method applies to models in IFC format, thus making control totally independent of the authoring technologies adopted in the asset design and implementation phase."
HOW
What approach did you take to building the solution?
Davide Cossu: "Our focus was on identifying a method to make the user autonomous in defining the rules to be used in the validation phase. Several scenarios were analyzed from which we selected the methods that would reconcile the necessary rigor with the flexibility required by real processes.
What we have set up makes it easy to define hierarchies of rules, lists of values, and constraints between metadata, through the loading of standard excel sheets. This "validation model," which translates the information model described in the information management plan, is related to the job order managed in Truspace and the different models that are part of it. This makes it possible to specialize control for each discipline model and each of its versions, making the control process during the project automatic until the as-built models are returned.
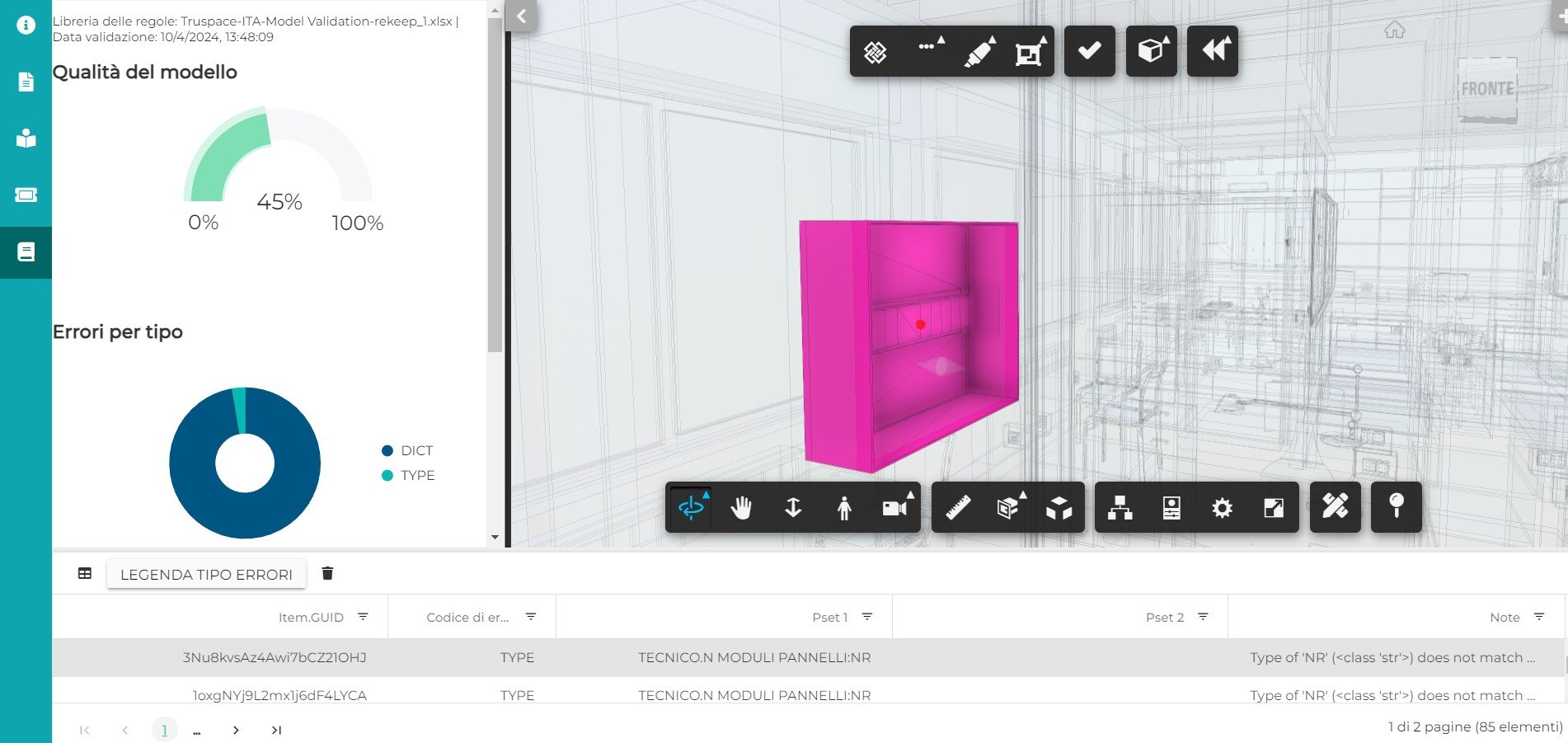
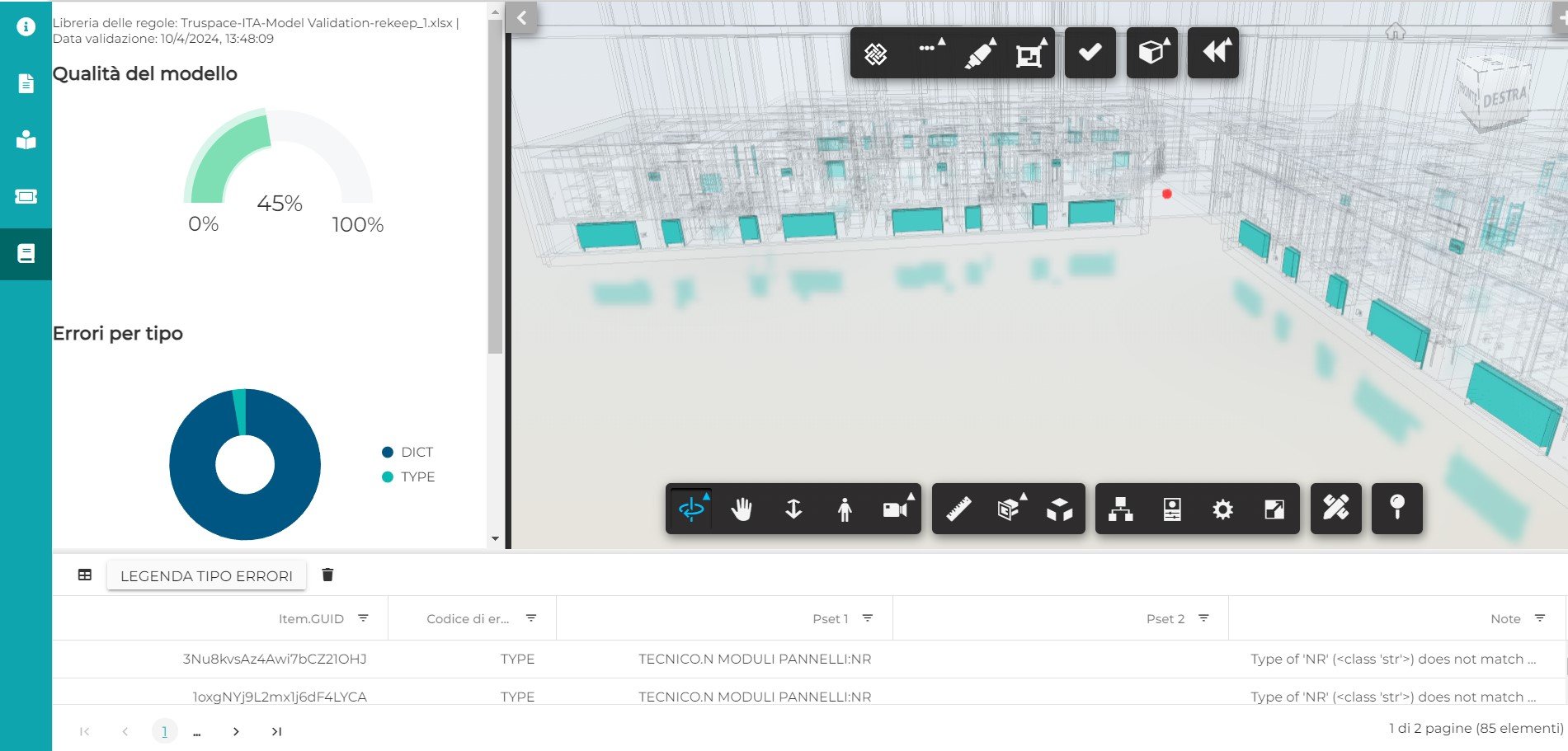
The output of the validation process can be consulted in the platform live or asynchronously being each report saved and historicized. The report allows the user to interactively consult the overall quality of the model with respect to what was predicted in the information management plan, the classification of errors found by type, and the detail of each individual error. These evidences are reported both as a list of non-validated items and interactively to model.
The final performance we obtained for the validation process was also excellent; once started, the evaluation report is available in a few moments in ordinary cases, and in a few minutes for more complex verifications and models."
FOR WHO
What are the benefits of this validation system and for which professionals?
Davide Cossu: "The method is defined and governed by those who coordinate the project and its information specifications (BIM Manager, BIM Coordinator), starting from the Information Specification and the BIM Execution Plan. The goal is to obtain models that are consistent with each other and equipped with the information necessary for the management processes (design, planning, execution, maintenance, etc.)
These rules have an impact on planners and designers who must from the outset include PSet and the required metadata within their designs, taking care to use dictionaries, values and constraints consistent with what is described in the information management plan.
The adoption of a flexible and documented on-board validation methodology allows, simultaneously and automatically without recourse to other tools, to:
- To the designer, author of the model, to self-verify and correct their delivery
- To the project coordinator to check and ensure the overall quality of delivery (design team, as built, etc.)
- To external verifiers to focus on technical quality of projects, not informational quality
Next steps
The function was fully released in early 2024 and is in use in several major projects.
Our focus next will be on refining the functionality to ensure ever greater ergonomics for users and on the study and adoption of the recent standard IDS (Information Delivery Specification) of BuildingSmart to keep Truspace consistent with international standards and their evolutions, among the strategic and primary focuses of the platform development roadmap.

